DeepRange and 7Series P&A System
Wild Well announced that its DeepRange tool, in conjunction with its 7Series riserless intervention system, has successfully performed full plug and abandonment operations on five subsea wells in the Gulf of Mexico. These wells are a part of a larger plug and abandonment campaign which began earlier this year.
While regulations have mandated cutting and pulling the wellhead in shallower water depths, waivers have been granted to allow them to be left in place. Wild Well strongly encourages leaving wellheads intact not only because of the costs of wellhead cutting and associated operational issues, but also to allow well re-entry in the future. A severed subsea wellhead cannot be re-entered.
Reduce Your P&A Liability with the Subsea P&A
Combining the Wild Well DeepRange Cementing tool with our 7Series Intervention System creates an unparalleled plug and abandonment (P&A) system that delivers a highly cost effective and regulatory-approved, rigless and riserless package.
Requiring only a multiservice vessel for deployment, our P&A system offers a field proven alternative to conventional, rig-based P&A operations while delivering enhanced performance.
Rapid Mobilization, Reliable Operation
For 40 years, Wild Well has supplied operators with industry-leading service whenever and wherever it’s needed. The Deep Range and 7Series continue that dedication to quality operations by offering subsea P&A services to a wide-range of applications.
Covering Every Step of Your Subsea P&A Operation
Step 1: Pre-operational engineering and planning comprises creating and resolving interfaces with the well and vessel of choice, developing detailed operating procedures, and creating a project execution plan.
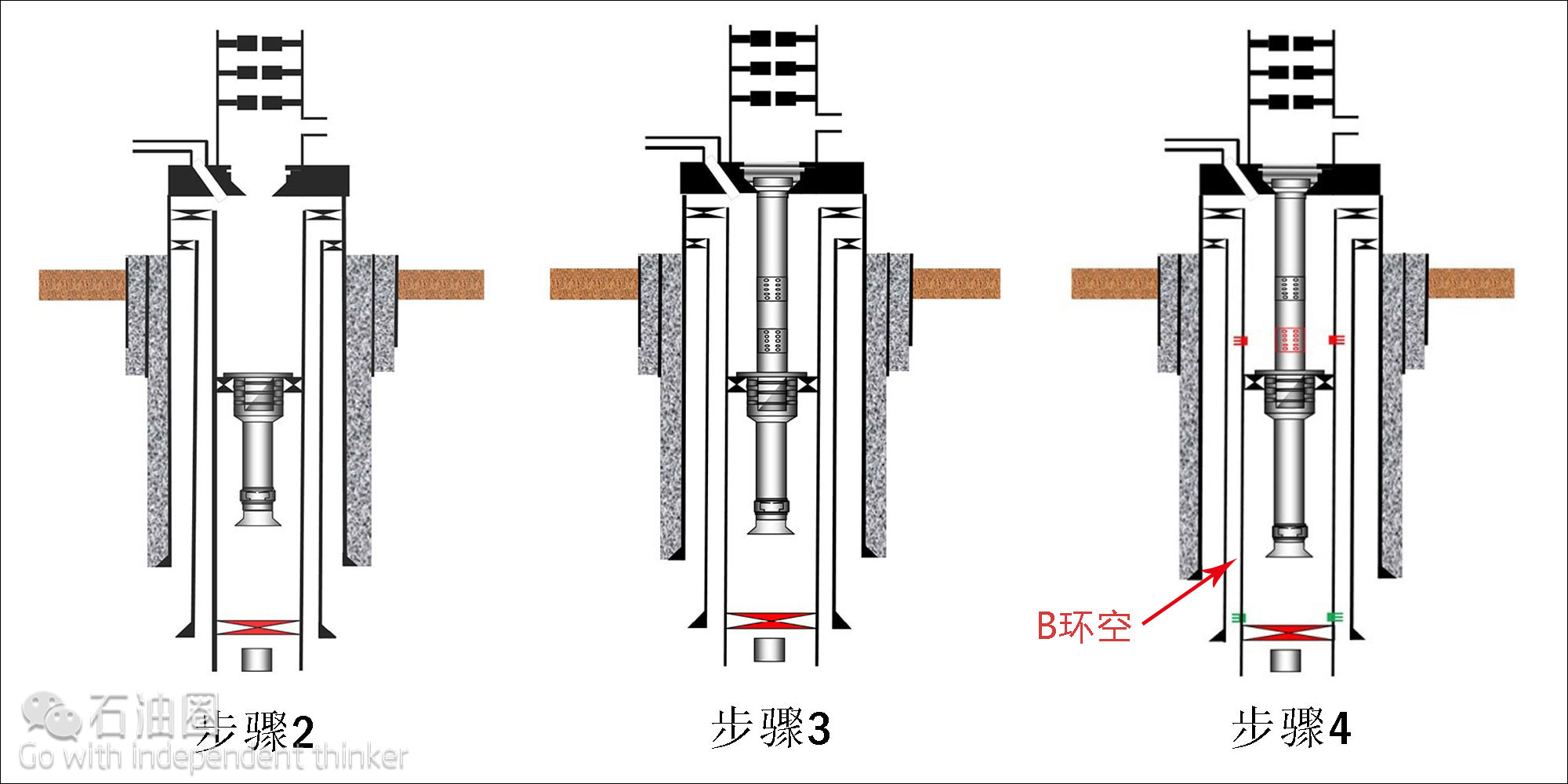
Step 2: Crews perform the temporary abandonment of the well, cutting and pulling the tubing before installing a cast-iron bridge plug and packer.
Step 3: The upper abandonment – consisting of an isolation bushing, tubing-conveyed perforating guns, and a seal assembly – are landed and latched into the packer.
Step 4: Perforation charges are deployed on eline and are used to perforate the tubing into the B annulus.
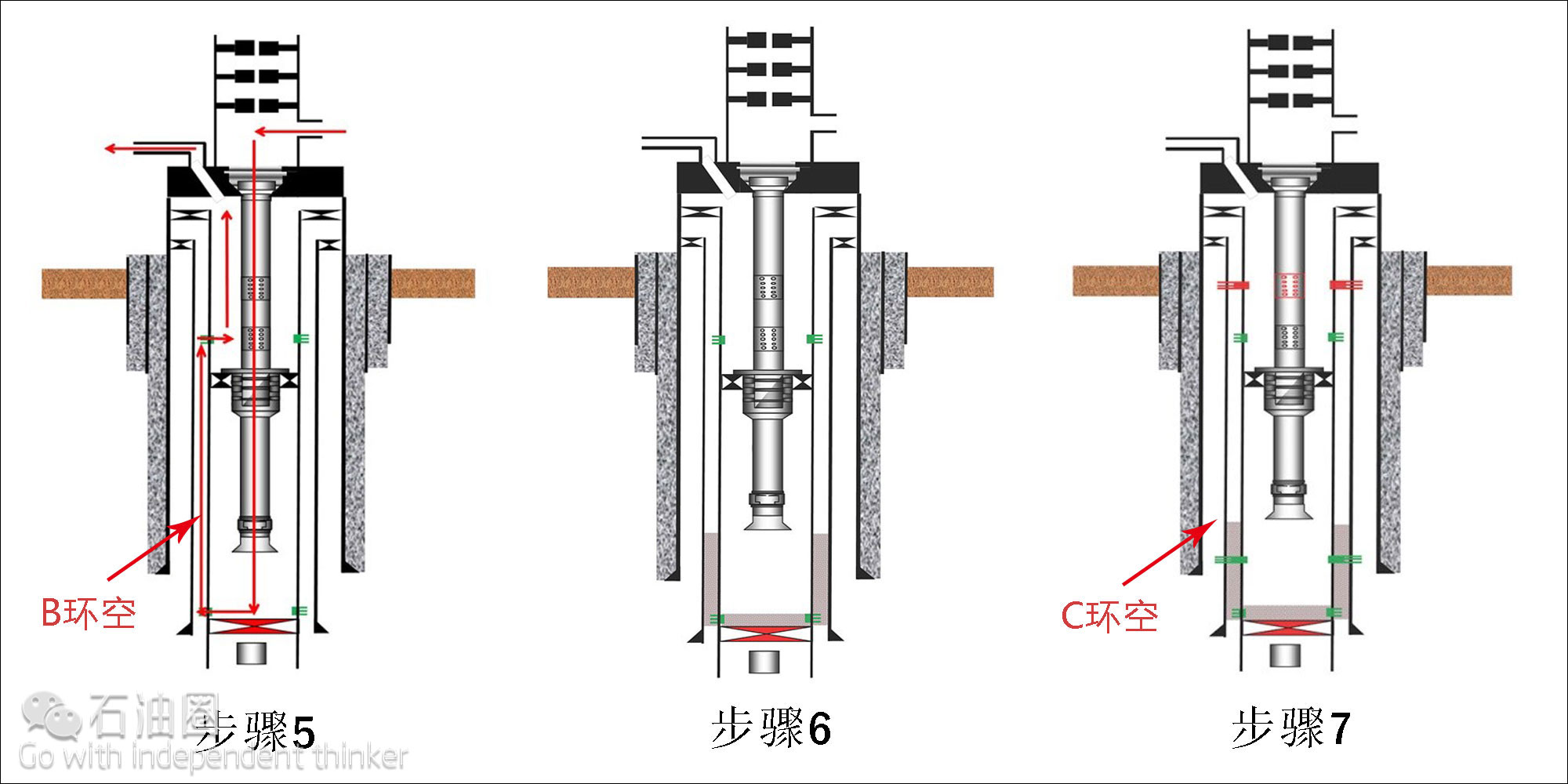
Step 5: Circulation is established through the tubing, into the lower perforations, up the B annulus, out through the upper perforations, and back up the production annulus. The isolation bushing diverts flow to the return lines.
Step 6: The binary plug is circulated into the B annulus. After waiting on the cement to harden, a mandatory pressure test is performed on the tubing and annulus of the plug.
Step 7: Circulation is established through the C annulus by firing the previously set, tubing conveyed upper perforation guns and eline conveyed lower guns.
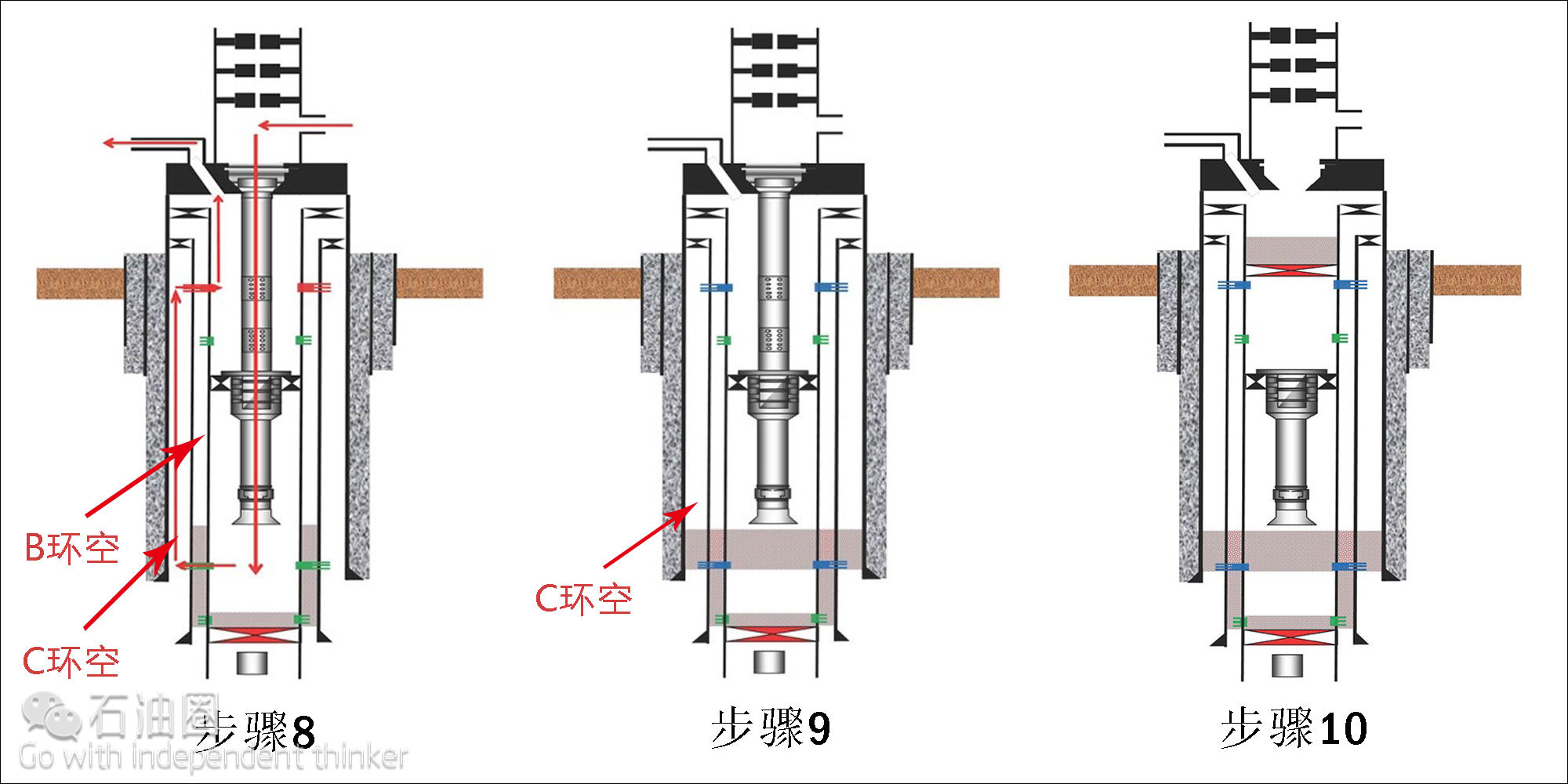
Step 8: Circulation is established through the C annulus as with the B annulus before.
Step 9: The binary plug is circulated into the C annulus. The plug is left in a “balanced” condition with the production annulus. After waiting on the cement, testing is performed.
Step 10: The upper abandonment assembly is unlatched from the packer and pulled from the well. A cast-iron bridge plug is set above the highest perforations and cement is bailed as per regulations.
Hardware Highlights
7Series Intervention System
1.Certified to 10,000 ft and 10,000 psi maximum working pressure
2.Redundancy in the environmental and well barriers
3.Shear seal ram can shear almost any tool string, including 3?-in., 135,000 psi drillpipe
4.Dual redundant controls systems
5.7+3/8 bore handles the largest crown plug
DeepRange Cementing Tool
1.Rigless, riserless
2.Resilient binary plug using resin and cement
3.Coiled tubing circulation to wellbore
4.Proven tooling methodology
5.Robust, ROV-driven technology
6.Minimally invasive procedure that maintains wellbore integrity
Reduce the Costs
The entire DeepRange operation takes place from a multi-service vessel that contains approximately 1000 m2 of back deck, a moonpool, working-class ROVs, and a heave-compensated knuckle boom crane with 60 t capacity at depth.
While on the topic of costs, a general cost figure of US$12 million per well can eliminate these P&A liabilities from the operator’s balance sheets. While the total cost can vary slightly given the total amount of work and configuration of the well and production system, it still represents a significant reduction in P&A cost.
Wild Well remains one of the only companies to combine senior well engineers, subsea engineers, regulatory experts, cementation engineers, and experienced wellsite personnel all in-house and all working towards the goal of reducing the costs of subsea P&A. In conjunction with the tried and true 7Series, DeepRange technology represents a significant opportunity for deepwater operators.
Properly performed subsea P&A operations deliver a safe, reliable solution to well decommissioning. New technology such as the DeepRange system provides offshore operators with a viable alternative to conventional P&A while ensuring minimal impact on the environment.
Expectations Exceeded on Riserless P&A Campaign in GoM
Cementing tool is certified to depths of up to 3,048 m and a maximum working pressure of 10,000 psi.
Anine-well plug and abandonment (P&A) campaign in the deepwater Gulf of Mexico (GoM) by Wild Well Control Inc. already has seen work on five subsea wells successfully performed using the company’s DeepRange cementing tool.
Used in connection with its 7Series riserless intervention system, the company is employing the rigless technology in water depths of up to 2,134 m (7,000 ft). In a presentation at a press conference at OTC, Wild Well Control said its tool is certified to depths of up to 3,048 m (10,000 ft) and a maximum working pressure of 10,000 psi.
According to Martial Buguieres, Wild Well’s vice president of marine well services, “The new tools and techniques used on this project already have exceeded expectations. Our methods offer reduced costs while maintaining full BSEE [Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement] compliance.”
Each of the wells used the new DeepRange tool to isolate an outer annulus by perforating and then circulating a minimum of 61 m (200 ft) of cement in place and pressure testing the binary plug as per BSEE regulations. “This is not a ‘perf and squeeze’ tool,” the company stated in the presentation.
The technology and methodology will help operators reduce their subsea P&A liabilities, it added, as riserless operations represent dramatic cost reductions when compared to traditional subsea P&A operations.
About Wild Well
Wild Well, a Superior Energy Services company and a global leader in well control and engineering services, outlined in its presentation that the GoM campaign presented “significant technical issues,” including extreme water depths, gas wells prone to hydrate formation and tree communication/control issues. New tools and techniques developed to overcome these challenges included a concentric circulating system, a well intervention controls system and extensive hydrates prevention/mitigation procedures.


 石油圈
石油圈