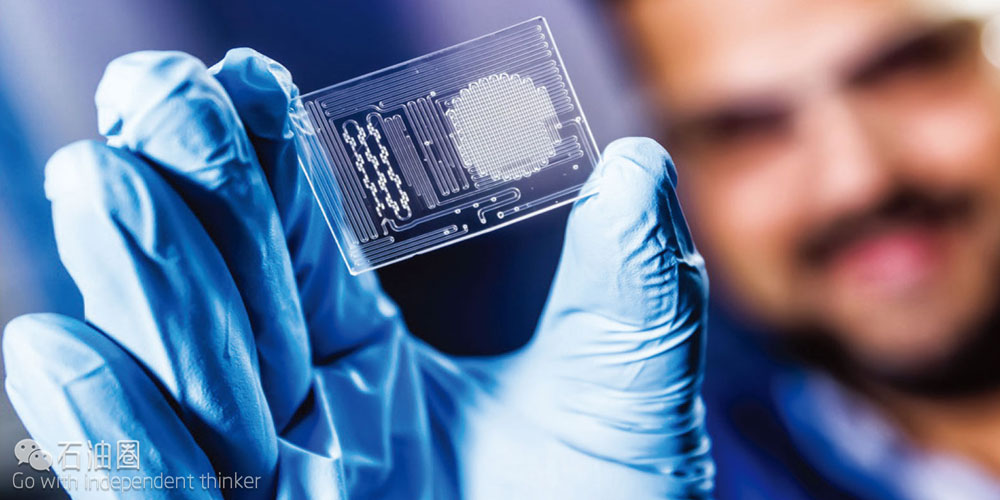
Maze* microfluidic SARA analysis delivers full automation when testing any oil sample for saturates, aromatics, resins, and asphaltenes (SARA)—providing repeatable and reproducible measurements while decreasing both turnaround time and use of solvents by more than 85%. This first commercial application of microfluidic technology to the oil and gas industry has been accepted by ASTM International Standard D7996 for asphaltene content measurement.
During Maze analysis, asphaltenes are measured using a proprietary microfluidic chip, followed by identification of saturates, aromatics, and resins using a miniaturized chromatographic column. Each fraction measurement is achieved through application of optical absorbance measurement using spectrometer and refractometer technologies.
The automation provided by Maze microfluidic SARA analysis removes operator dependency and subjectivity from the measurements, improving analysis integrity and data quality. Microfluidic technology also standardizes the amount of solvent required for each analysis—offering superior precision across measurements—while significantly reducing the overall volume of solvents used and reducing HSE risk to personnel.
Results from the Maze analysis have industry-wide applications, including understanding of the oil’s physical and refining properties, assessing crude oil value, supporting flow assurance studies, validating sample quality prior to PVT analysis, and supporting gradient and compartmentalization as well as geochemical studies.
Enables repeatability and reproducibility
Maze microfluidic SARA analysis is a two-part process. For asphaltene content analysis, oil is titrated with excess of nonpolar solvent (n-heptane) to force asphaltene precipitation, which is filtered and separated through the microfluidics chip. The visible spectra of oil before and after precipitation is measured through a spectrometer, and the difference in optical absorbance is correlated with the gravimetrically measured asphaltene content of the sample. This process is completed using the microfluidics chip and automated pumps, providing repeatable and reproducible optical absorbance for high-quality asphaltene content measurements.
Once the asphaltenes are measured, the deasphalted oil (maltenes) exits the microfluidic chip and is displaced onto a miniaturized chromatographic column loaded with a stationary phase. The mini-column is then sequentially washed with various solvents to separate fractions of saturates, aromatics, and resins. The refractive index of the saturate fraction and the optical absorbance of the aromatic and resin fractions are measured using a refractometer and spectrometer. The refractive index of the saturate fraction correlates with the mass of the fraction. Similarly, the optical absorbance of the aromatic and resin fractions correlate with the mass of the fractions.
Ensures certainty across measurements
Conventional SARA analysis requires extensive time and material resources, liters of solvents, and a large laboratory footprint. Results vary widely from lab to lab due to slight procedural and equipment modifications, operator competency and efficiency, and chemical purity and availability. With Maze microfluidic SARA analysis, conventional methods—which are cumbersome and time consuming—are now automated, removing operator dependency and subjectivity from the analysis. This ensures certainty across measurements for high-quality results that are always repeatable and reproducible.
FEATURES
1.First application of microfluidics technology to the oil and gas industry
2.Accepted by ASTM International Standard D7996 for asphaltene content measurement
3.Fully automated process removing operator dependency
4.Less volume of solvent required
5.Smaller footprint by avoiding use of bulky glassware
6.Fraction measurement using spectrometer and refractometer technology
BENEFITS
1.Delivers high-quality fraction measurements of saturates, aromatics, resins, and asphaltenes
2.Ensures accuracy, repeatability, and reproducibility
3.Improves analysis turnaround time with rapid SARA measurements
4.Reduces HSE risk by minimizing exposure of personnel to solvents
5.Ensures consistent measurements for the sample chain of custody
6.Provides alternative to cumbersome and time-consuming conventional methods
CASE STUDY
Maze Analysis Delivers Consistent SARA Measurements Using Industry-First Microfluidic Technology
New SARA analysis method needed
The industry’s standard method for conducting SARA analysis of oil samples in the laboratory was causing problems for operators in terms of time and reliability. Available test methods were cumbersome and time consuming—taking 3–5 days on average to complete. In addition, slight procedural and equipment modifications, laboratory technician competency and efficiency, and chemical purity and availability were constant challenges in obtaining reproducible results.
With SARA analysis being widely used across the industry—from validating oil samples prior to PVT analysis to supporting flow assurance and geochemical studies—it was important to develop a new method to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the measurements.
Maze microfluidic SARA analysis developed
With the challenges of conventional SARA analysis fully understood, technical experts across Schlumberger’s global network of research centers and reservoir laboratories developed Maze microfluidic SARA analysis as the next-generation, fully automated solution. Asphaltene content is first determined using proprietary microfluidics chip and spectroscopy technologies, followed by identification of saturate, aromatic, and resin fractions using a miniaturized chromatographic column coupled with refractive index and optical absorbance measurements.
Accepted by ASTM industry standard
The automation provided by Maze microfluidic SARA analysis eliminates laboratory technician dependency for precise fluid measurements that are always repeatable and reproducible. Turnaround time for Maze analysis is only 4 hours compared with conventional technology at 3 to 5 days, and use of solvents is decreased by more than 85%. This new method improves accuracy and efficiency of SARA analysis enabling better-informed decision making—with upstream to downstream applications.
Maze microfluidic SARA analysis is the first commercial application of microfluidic technology to the oil and gas industry, and it has been accepted by ASTM International Standard D7996 for asphaltene content measurement.
CHALLENGE
Improve the reproducibility, repeatability, and turnaround time when analyzing oil samples for saturates, aromatics, resins, and asphaltenes (SARA).
SOLUTION
Employ new Maze* microfluidics SARA analysis built on novel microfluidics and spectroscopy technologies.
RESULTS
1.Achieved ASTM International Standard D7996 for asphaltene content measurement.
2.Developed a fully automated process, removing operator dependency from the analysis.
3.Reduced turnaround time from 3 to 5 days to only 4 hours and reduced required amount of solvent by 85%.


 石油圈
石油圈