APS InField Liner(IFL)
Internal corrosion may cause a pipeline to prematurely reach the end of its useful service life before its intended design life, which will then necessitate either early pipeline closure or total replacement. Historically, there has been no viable means for installing an internal corrosion barrier into an existing hydrocarbon subsea pipeline once it has been laid.
PETRONAS & ANTICORROSION PROTECTIVE SYSTEMS (APS) concluded a three year multi-million dollar research & development program to develop the materials, means and mechanisms for the in-situ placement of flexible tight fit rehabilitation corrosion barriers. This development program was concluded and has since led to the successful deployment of IFL.
The IFL liner is a flexible Kevlar reinforced liner that can be pulled in over long lengths in a single pull. The usage of high specification materials within its construction provide the IFL system with a high resistance to a wide range of hydrocarbon media at elevated temperatures of up to 110°C and exceptional host pipe matching pressure retaining capability within its tight fit operating criteria. The IFL system thus now offers the subsea pipeline industry with a supremely viable, fast and economic preference when compared against the only other option of a new-lay pipeline replacement.
IFL Product Range
Application: IFL can be utilized in very aggressive, hot, sour hydrocarbon service conditions of up to 110 degrees centigrade.
Diameter range: Ranging from 6” to 18”.
Liner length: Single liner lengths available in multiple kilometres.
IFL Liner Matrix
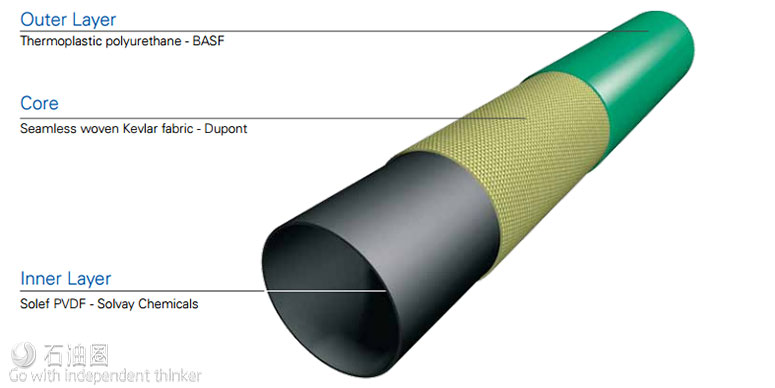
The IFL liner comprises of a Solvay Solexis PVDF inner liner a tightly woven Aramid core, using Dupont Kevlar fabric, with an outer layer of abrasive resistant Thermoplastic Polyurethane from BASF.
Key Benefits
(1)Cost-Effective Compared to New Lay
(2)Saves Time in Design, Planning and Installation
(3)Extends Pipeline Service Life > 30 Years
(4)Protection of Environment Due to Dual Containment
(5)Multiple IFL Systems Already Installed in Hydrocarbon Subsea Pipelines
Technology in Line
(1)Multiple Kilometers Installed in Single Pull
(2)Accommodates Multiple 90° Bends
(3)Resistant to Hot Sour Crude Oil and Sour Gas
(4)High Temperature Resistance up to 110°C in Hydrocarbon Exposure Conditions
(5)Extremely High Resistance to Permeation
Markets Served
The IFL system is ideal for rehabilitating in-field subsea pipelines running from platform-to-platform, or from platform to shore. IFL can also be used as a corrosion barrier for new pipelines which will be known to be exposed to extremely corrosive environments incurred due to aggressive environmental influences such as SRB or in combination with high water cuts, and thereby significantly reducing the predicted life-span of the pipeline without the application of a fully effective corrosion barrier.
The IFL system was originally developed as viable and cost-effective method for subsea pipeline rehabilitation, however and in addition to this, the IFL system may also have specific applications for the onshore hydrocarbon pipeline industry as well. An example of this would be where a pipeline passes under an area where, for one reason or another, site access is extremely limited, and thus the pipeline has to be rehabilitated over much longer lengths with single pulls.
Fields Of Application
Rehabilitation of existing subsea hydrocarbon (also water injection) pipelines which have naturally reached the end their designed service life.
Rehabilitation of existing subsea hydrocarbon (also water injection) pipelines, which exhibited signs of early failure, due to higher than expected rates of corrosion.
Abandoned or decommissioned subsea hydrocarbon (also water injection) pipelines, whereby the IFL system offers the possibility of re-commissioning these very pipelines.
The installation of an IFL Liner inside of new hydrocarbon subsea pipelines in circumstances where extreme corrosion conditions are known to exist.
Rehabilitation of onshore hydrocarbon pipelines whereby the pipeline is required to be rehabilitated over long lengths, due to the inability to gain access to the pipeline at shorter length intervals.

 石油圈
石油圈