As human beings, we suffer from loss aversion, where we are more afraid of loss than we are motivated by making a gain. In the oil and gas industry, where the sums of money involved can be high and the consequence of failure can be catastrophic, this tendency is exaggerated by the fact that costs are guaranteed but rewards can be uncertain. This leads us to define work in terms of definite costs, rather than possible gain. For example, drilling is often measured in terms of “cost per foot,” rather than in terms of “cost per barrel produced.” In doing so, we can miss out on getting the best return from our assets.
Aversion to risk means that the oil and gas industry has, historically, taken many years to take on-board new technologies, even when they have demonstrable benefits. Directional, underbalanced, coiled tubing drilling is one of the technologies that has all of the benefits, but has remained a niche application. Multi-year projects have been on-going in Alaska since the early 1990s, and in Saudi Arabia since the middle 2000s, and there have been other, shorter-term projects, both on land and offshore. These have proved successful, as demonstrated by their long-term nature. Uneconomic projects don’t last very long. Despite there being hundreds of thousands of depleted wells, where the benefits of underbalanced CT drilling are very applicable, so far, the technology has not entered the mainstream.
There was a time when other technologies also were looked at in the same way. These days, nobody thinks twice about horizontal drilling. In fact, some younger drilling engineers might be forgiven for thinking that the only way to drill a well is horizontally. Despite the technology being introduced in the early 1990s, it took until 2010 for horizontal wells to really take off and, these days, 77% of the most prolific wells in the U.S. are horizontal. Coiled tubing has made steady advances, in terms of reliability and services, and is now considered mainstream technology.
It takes a market jolt to spur the adoption of newer technologies. In boom times, costs rise, and this doesn’t help the introduction of new technology, because the cost-savings can get swamped by the increasing prices. One thing that characterizes all of these technologies is the fact that they all cost more than the technologies they replace, but the increase in productivity ultimately makes the extra investment worthwhile. In no case, would anyone, especially not an accountant, have advocated their introduction, if they had just considered their day rate cost, alone. So, we need to evaluate the benefits of new technology fairly with the costs.
OVERLOOKED PRODUCTION
It is currently an attractive option to re-work existing wells with an intervention, to increase production. Re-working a well at least takes away the uncertainty of whether there is a productive oil or gas zone to be accessed, which can be a risk with a new well. One potentially rewarding way is to cut a window in the production casing of a vertical well, and to drill horizontal laterals in underbalanced conditions with CT. In some cases, this technique has increased production by a factor of five.
Directional coiled tubing drilling brings together horizontal drilling, underbalanced drilling and coiled tubing to benefit from all three technologies. Coiled tubing is specifically designed for working under pressure so it is ideal for underbalanced drilling where maintaining the correct pressures is critical to protecting the reservoir. In fact, coiled tubing drilling is the only way to ensure the well is kept underbalanced at all times, because the operation does not need to stop to make connections.
With underbalanced drilling come the benefits of increased drilling speeds, reduced lost circulation and differential sticking problems and, a key advantage, the reservoir is protected from formation damage. Reduced problems translate into lower project risk, which is a key requirement when the efficiency of a project is vital to its economic success.
But underbalanced drilling with CT is more complex and less familiar to most. There is a natural tendency to ask, “how much will it cost?” before asking the question, “what’s the payback?,” which is what really matters. In the process, economic opportunities might be ignored.
Fortunately, it’s relatively straightforward to combine the most significant factors in terms of cost and, importantly, revenue, to evaluate whether an intervention is worth doing. By taking into account the timing of both costs and future revenues, it is possible to see when an intervention will break even, what future revenues will be after that point, and, consequently, the IRR for the project. This can be done with a simple spreadsheet model, and it helps to concentrate on the return on investment before considering what it is worth spending to achieve that return.
THE FORWARD-LOOKING MODEL
The model used is dependent on four factors:
The production increase that might be expected by drilling a horizontal well instead of a vertical well.
The oil price.
The total cost of the intervention.
The decline curve of the well.
The production increase. The Productivity Index is a function of the length of reservoir drained by a well. Horizontal wells contact more of the reservoir, so they can give higher productivities in laterally extensive reservoirs. As an estimate of the extra benefit of drilling a horizontal well you can use the Productivity Improvement Factor (PIF), which compares the initial productivity of a horizontal well to that of a vertical well in the same reservoir, during early-time radial flow. The PIF is defined as:
Assuming that horizontal and vertical permeability are the same, and that the reservoir is 40 ft thick and the horizontal section is 400 ft long, then the PIF would be 10. This is a theoretical value and, based on historical data, a PIF of between 3 and 4 should be considered to allow for the uncertainties inherent with drilling a horizontal well, potentially for the first time.
The PIF assumes that the wells will be drilled overbalanced, and that underbalanced drilling would not offer any further production increase. Underbalanced or at-balance drilling can increase the ROP greatly when drilling, and therefore reduce the drilling time. Coiled tubing drilling is well adapted to UBD.
The oil price should be taken on a best-guess basis. It is a variable and can be changed to see the sensitivity of the payback and, therefore, the risk that can be tolerated. Clearly, a higher oil price will allow a shorter payback time, and a lower oil price will extend the payback time. If you had a crystal ball and could predict future oil prices, the value could be varied over time. So, in most cases, short term payback is the governing factor in deciding about an intervention.
The total intervention cost. This is the value that is effectively being determined. It also can allow for production during the drilling process. Better technology that will produce a better result may be just the ticket, but it needs to be affordable for the well under consideration.
Some wells will be past the point where an intervention is economically viable. Knowing the maximum amount that can be spent economically on a well to achieve the desired payback dictates the intervention that might be considered, and the subsequent discussions with the appropriate service companies. The cost of chasing a wild goose is not negligible.
The decline curve. Every well is different, but they will all decline after initial production. So, being precise about the exact form of a decline curve is not particularly important when doing comparative calculations. Its main purpose is to avoid grossly over- or under-estimating the returns over time. A decline curve that exponentially reduces production to a certain percentage, after the first year, is as good as any, but this can be changed easily, based on known field data.
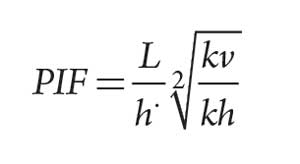


 石油圈
石油圈
