眼见为实。当地下的油藏密码被技术破解时,也就没那么神秘莫测了。
来自 | E&P
编译 | 张德凯
众所周知,油价下跌迫使页岩开发商提高效率,其中包括钻井方案和完井设计优化。在往常的作业中,开发商通常会放弃使用地震勘探工具,因为他们觉得已经对油藏有了足够的认识。然而事实并非如此,在实际的钻井作业中,通常发生无法准确钻遇油气甜点的情况,分支井以及射孔作业的设计难度极大。
迫于低油价的压力,结合作业经验,勘探工具在当今页岩开发中的应用得到了前所未有的普及。在墨西哥湾的作业中,勘探工具能够准确分析盐丘以下页岩油藏的复杂组成。地震勘探数据内容非常丰富,对于油藏性质解析能够起到关键作用。例如,地震勘探数据能够预测钻井风险多发地层,并能识别高裂缝密度地层。将地层性质与岩土力学性质结合,即可获得更准确的地层压力信息,更准确地预测其对产量的影响。
新型模型提高复杂油藏模拟准确性
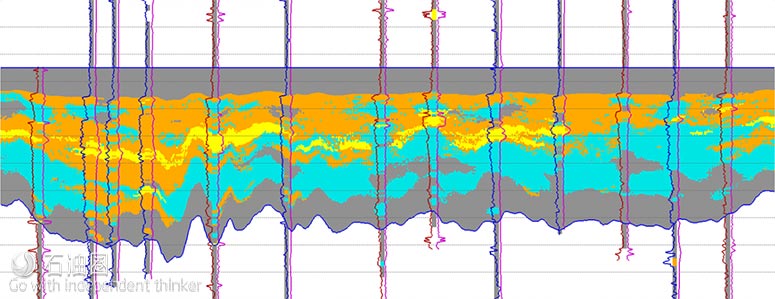
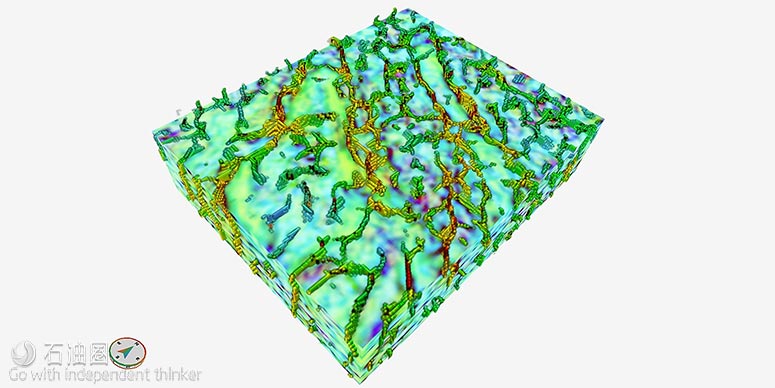
RockMod模型分辨率更高,上图为Powder River盆地地层的砂层(黄色)和非常规砂层(橘色)分布
CGG GeoSoftware公司在多种类型油藏(包括复杂的非常规油藏)模拟方面都有先进的技术。其中,Jason Rock-Mod地统计学反演法模拟技术已经得到了现场应用的验证,在复杂油藏的应用中非常有效,建立的油藏模型分辨率极高,对于钻完井设计及生产预测都起到了非常重要的指导作用。地统计学反演法根据不同的计算原则将不同油藏的地质信息整合,包括岩石物理测井数据、地震勘探数据以及地质概念等,模型对于岩相/油藏岩石性质的预测更准确,而且模拟结果同时包括井筒及井间数据。我们都知道,非常规油藏的地层性质波动极大,包括垂直/水平方向的岩相/岩层机械性质等,所以上述模型数据就显得格外重要。
新型模拟软件的强大功能得益于RockMod对输入数据的精准处理以及优秀的分析功能,模拟结果与岩相及岩层性质的分析/预测都非常准确。RockMod的一大特色是采用了Markov Chain Monte Carlo随机反演功能,通过岩石物性模型,同时实现了地层弹性数据、油藏的岩相分析,这对于复杂油藏岩相的分析、解译非常有效。此外,模拟结果可通过角点网格方式显示,有常规和放大两种模式,可直接用于静态模型集成和井筒作业设计。
新方案识别非常规油藏
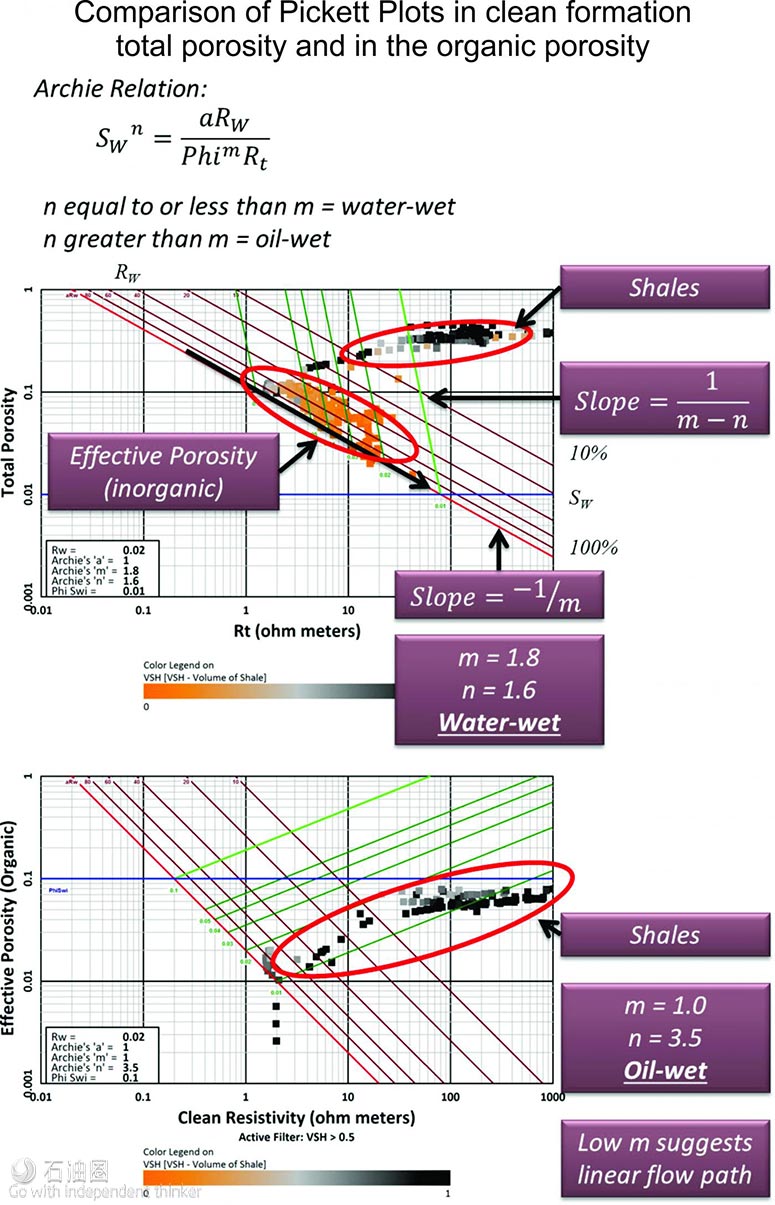
通常来讲,非常规油藏的润湿情况复杂,同时存在亲水/疏水组分。岩心性质分析一直作为油藏润湿性质分析的主要手段,然而,在当前测井工具的基础上,还没有一款适合的岩石物理技术能够将岩心按照润湿性质分类。在2016年拉斯维加斯举行的美国石油地质学家会议中,Digital Formation公司根据多种非常规油藏数据,利用三重测井技术,提出了一种孔隙分类方案,可将岩石孔隙组分分为水润湿和油润湿型。
其中,油润湿型孔隙基本为有机孔隙,是地层热演化过程中总有机碳变化产生的。而在该技术出现之前,利用常规的岩石物理分析还无法得到油基孔隙的具体数据,利用Digital Formation提出的方法,非常规油藏的流动性质研究会取得更加准确的成果,实现油润湿型/水润湿型孔隙的层级量化。由于每种组分的流动性能都不同,根据孔隙量化结果,即可得到整体油藏的流动性质结果。
叠前稀疏脉冲AVO反演技术
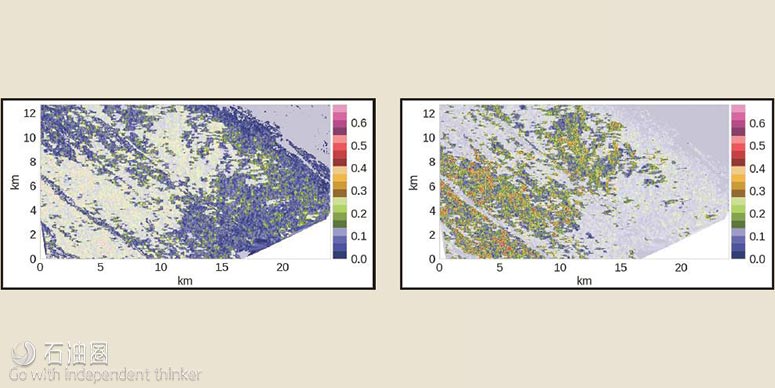
Geokinetics公司的AVOz反演能够进行油藏放大/补偿各向异性的模型独立表征,对油田人工智能、放大定量解析及油气甜点识别都具有重要意义。该分析流程源自方位角AVO反演数据驱动模式,利用人工智能对甜点属性进行分析,之后对甜点地层结构进行解析。由于地层属性与模型是相互独立的,分类与聚类不会受限,使模型(如Ruger)的假设条件和模糊点更少,准确度更高。稀疏Bayesian(贝叶斯)参数的应用能够防止叠前区块的过度评估。此外,在该模型中还采用了一种新型的Euclidean参数,以保持模拟过程中方位角自由度的旋转不变性。目前,由于Bayesian模型只对地层稀疏参数低反射面的光滑度进行假设,应用简单,应用非常普遍。
页岩油藏地震勘探数据价值最大化
在北美的陆地页岩油藏开发中,井筒数据非常丰富,基于此,地质学家可进行分层数据、水平井段数据与性质分布的关联,之后建立模型。尽管井筒数据已非常丰富,地震勘探数据必不可少,那么有哪些信息是其他井筒信息无法提供的呢?地震勘探数据对故障预测极其重要,故障包括定向钻井中的相关风险、高缝隙密度区块等,还设计提高采收率问题。当前又出现了一种新的故障网络理解方式—全面认知解读。认知解读是通过控制思维中的认知能力和现代阐释技术的计算能力,对地层信息进行快速、准确的解译。
通过结合不同断层性质数据,地质学家可得到断层类型等信息,进而对地层属性就可得到更全面的认识。配色方案对于识别一幅图表中不同数据源中的新型非常有效,将三种地层缺陷属性分别以青色、品红、黄色(CMY)表示,根据颜色变化可快速获得断层属性和差异信息。在CMY减色法识别断层信息中,如果三种颜色断层信息都检测为错误,则会显示为黑色。
非常规油藏表征分辨率提高八个数量级
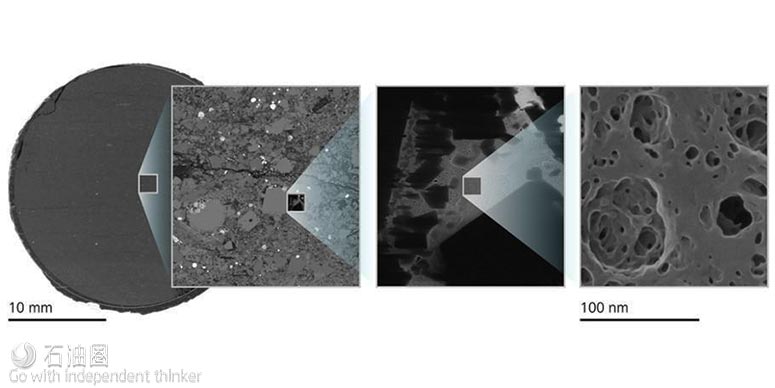
有机页岩孔隙的高分辨率表征,分辨率由25mm提升至纳米级别
Zeiss Microscopy Business Group的高分辨率显微镜可提供多种规格的图像分析表征,将油气工程师的岩心分析带入了纳米水平。此外,通过在单一分析平台配置不同工具,在放大分析的同时还可进行2D/3D光学、XRD及电子显微镜分析。获得这些数据后,与高级可视化、量化、模拟工具结合,即可得到孔隙率、孔隙结构、孔隙连通性、矿物学、矿物分布、裂缝分布及其他对碳氢化合物流动产生影响的地层岩石物理性质;然后进一步将这些信息用于油田或是整个油藏区块的模型建立,指导油藏的勘探开发及后期开采工作的进行。岩层矿物成分/组合的分析对于研究水力压裂影响也非常重要,利用这些数据,开发商和作业人员就能优化井间距,最小化完井失误率。
您也有让人挠头的难题需要解决,或是优质技术想要找应用市场吗?如果有的话,欢迎联系小编微信或邮箱,也许能找到一剂良药。
柠檬:186-2292-2332;weiyameng@fonchan.com
二丫:131-3255-0596;zhanglingyu@fonchan.com
For English, Please click here (展开/收缩)
The downturn has unquestionably forced shale operators to get more efficient, not only in their drilling programs but also in their completions designs. Gone are the days when tools like seismic were considered unnecessary in shales because operators already knew where they were. In fact, shales, being the contrary rocks that they are, have thrown up a huge learning curve in terms of finding the best places to land the laterals and place the perforations.
So subsurface sensing tools are entering the shale domain like never before. Tools that were designed to peek below the salt domes in the Gulf of Mexico are proving to be just as adept at clarifying the complexities of shale formations. Seismic data contain a wealth of information that can help explain these reservoirs. For instance, seismic data can help image faults to both avoid drilling hazards and characterize areas of high fracture density. Incorporating rock property and geomechanical information helps operators better understand the pressure regime in their reservoirs and how this might impact eventual production.
BETTER RESERVOIR MODELS IN COMPLEX PLAYS
CGG GeoSoftware powers multidisciplinary workflows for all types of reservoirs, including complex unconventional resource plays. Jason Rock- Mod geostatistical inversion has proved itself to be an effective tool in these environments, providing high-detail reservoir models to guide well planning and more confidently forecast production. Geostatistical inversion methods integrate geoscience data of different scales from different disciplines, such as petrophysical well log data, seismic data and geological concepts, to create models that predict lithofacies and reservoir rock properties more accurately, not only at well locations but between the wells. This is important in unconventional plays, where the subsurface exhibits significant variations in lithofacies and reservoir and mechanical properties both laterally and vertically. Multiple realizations of the model are generated by RockMod that honor the input data and are then analyzed with a ranking tool to assess uncertainty in facies and rock property estimates. Key differentiators for RockMod include a Markov Chain Monte Carlo stochastic inversion scheme, where facies are simultaneously inverted with elastic and reservoir properties through rock physics models. This enables very subtle facies interpretations in complex plays. In addition, model results can be delivered in a corner point grid format, with or without upscaling, for direct integration into static modeling workflows and wellbore planning activities.
METHODOLOGY DISTINGUISHES UNCONVENTIONAL RESERVOIR COMPONENTS
It is commonly recognized that unconventional reservoir systems have mixed wetting, both a waterwet fraction and an oil-wet fraction. Analysis of rock samples has been used for many years to measure reservoir wetting. However, there are currently no available petrophysical techniques for wetting categorization using readily available logging suites. In 2016 at the American Association of Petroleum Geologists meeting in Las Vegas, Digital Formation presented data from several unconventional reservoirs using triple- combo logs to categorize the porosity component that is water-wet while recognizing another component that is oil-wet. The oil-wet component is organic porosity generated from the total organic carbon during the thermal maturation process. This organic porosity has not been previously calculated in standard petrophysical analysis. The approach has very significant applications to the study of the flow characteristics of unconventional reservoirs. The amounts of porosity that are oil-wet and water-wet can be quantified level by level. Each component will have markedly different flow characteristics to derive a combined response for the total system.
A SPARSE PRESTACK AZIMUTHAL AVO INVERSION
Geokinetics’ AVOz inversion provides a modelindependent characterization of amplitude vs. offset (AVO) anisotropy enabled from the ground up to support artificial intelligence, augmented quantitative interpretation and interpretation of sweet spots. This analysis workflow extracts attributes of azimuthal AVO in a data-driven fashion, applies artificial intelligence to resolve structure in the attribute space and then provides interpretation of these structures. Because the attributes are model-independent, classification and clustering is not constrained to limiting assumptions and ambiguities of models such as the Ruger model. Sparse Bayesian priors are applied in the prestack domain to guard against overfitting. A novel Euclidean prior is derived to preserve the rotational invariances required by the azimuthal degree of freedom. The Bayesian prior model is very general, assuming only sparseness of the layered earth and smoothness of the reflectivity surface.
THE VALUE OF SEISMIC IN SHALE PLAYS
In onshore U.S. shale plays there is an abundance of well data, allowing geoscientists to correlate well tops, horizons and property distribution for model-building. With all of these well data, is seismic needed, and what can seismic tell us that the high density of well data doesn’t? Seismic data are extremely important for fault mapping. Faults can be a drilling hazard when geosteering but also define areas of high fracture density for improved recovery. A new way to understand the fault network is through cognitive interpretation. Cognitive interpretation harnesses the mind’s cognitive ability and the computing power of modern interpretation techniques to rapidly and accurately interpret geology. By revealing fault patterns through the blending of several fault attributes, geologists and geophysicists are able to gain a better understanding of the subsurface. Color blending helps identify the relationship between information from different data volumes in a single image. A blend of three fault attributes in a cyan, magenta and yellow (CMY) color scheme will rapidly provide new insights and distinguish greater detail from the variation in colors. Fault attributes using a CMY subtractive color scheme will result in black if all three fault volumes detect a fault.
CHARACTERIZING UNCONVENTIONAL RESOURCES ACROSS EIGHT ORDERS OF MAGNITUDE
Zeiss Microscopy Business Group’s oil and gas products include microscopes that provide a range of multiscale imaging solutions, allowing petroleum engineers to move directly from the whole core down to the nanopore and back up again by integrating 2-D and 3-D data from light, X-ray, electron and charged ion microscopy in a single multiscale correlative platform. These data are then linked with advanced visualization, quantification and modeling tools to give information on porosity, pore structure, pore connectivity, mineralogy and mineral distribution, fracture aperture distribution, and many other key petrophysical properties governing macroscopic hydrocarbon flow and transport. This information can then be used to better inform the creation of field- and basin-scale models, guiding ongoing E&P and development. Characterization of the rock’s constituent mineral assemblage also is critical for understanding how a sample will respond to hydraulic stimulation, enabling producers and operators to better design well spacing and minimize completion failure.
未经允许,不得转载本站任何文章:

 石油圈
石油圈





